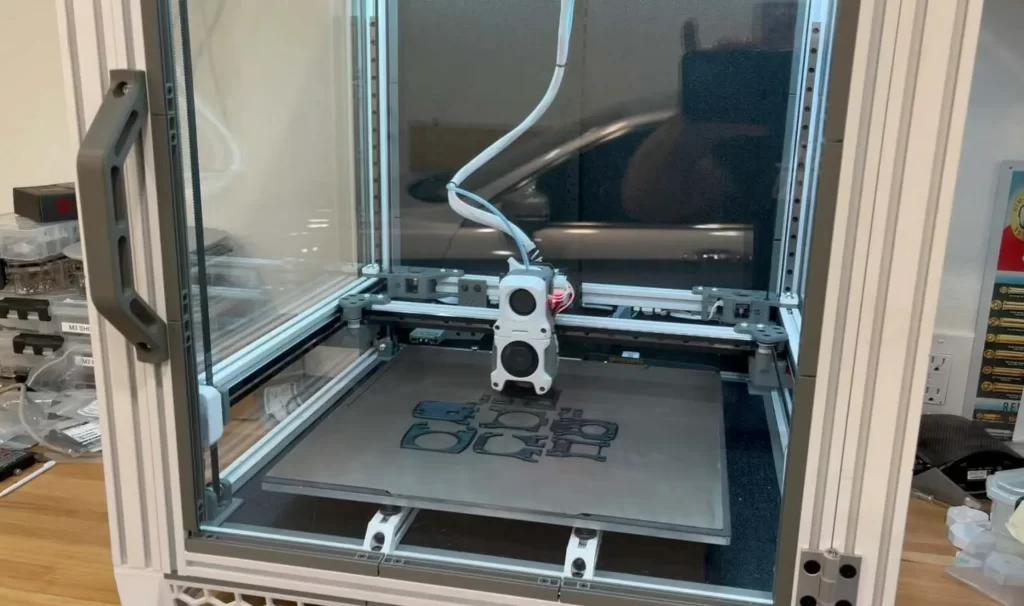
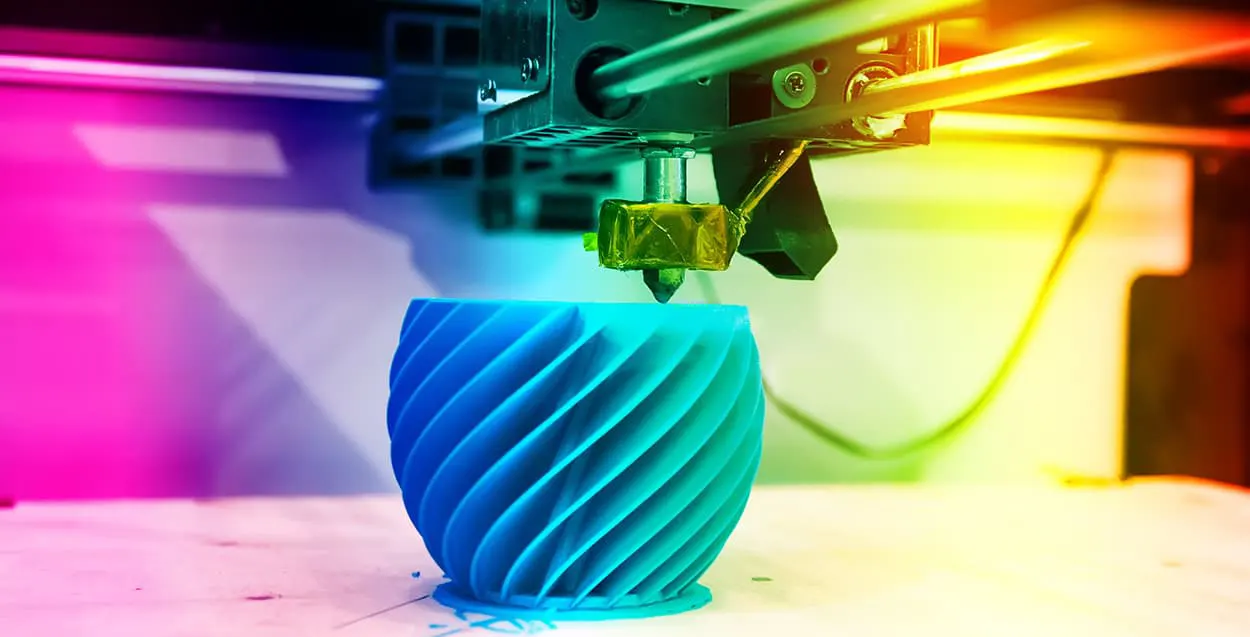
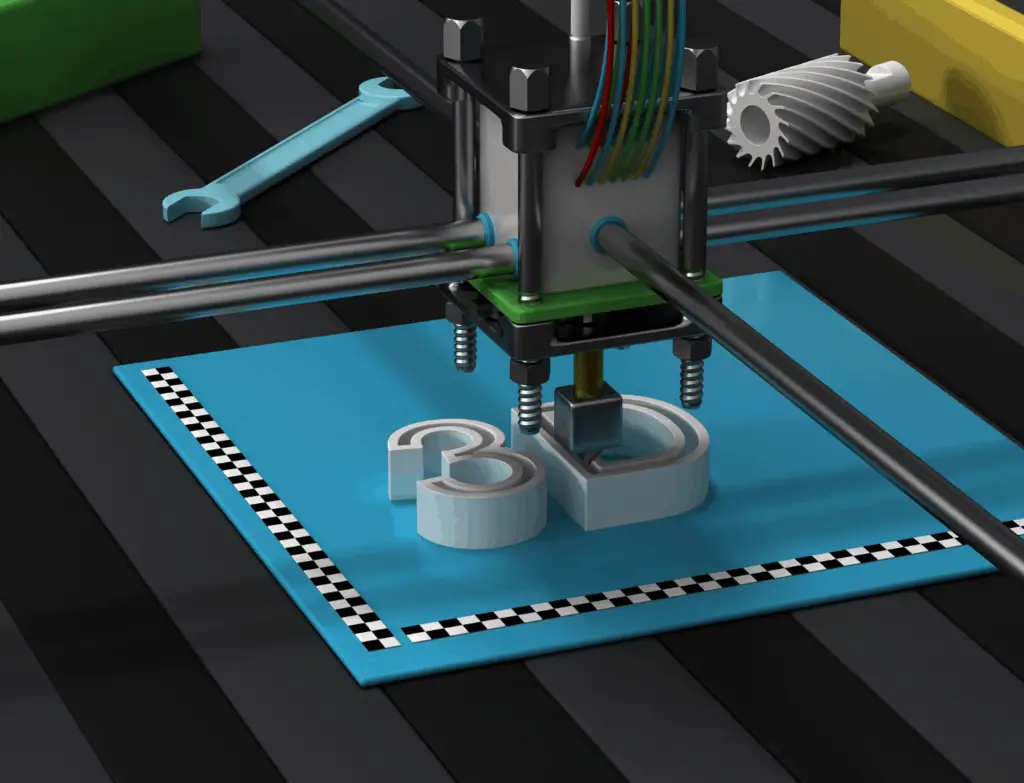
Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) 3D Printing, is also known under the trademarked term Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). This technology was invented after SLA (Stereolithography) and SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) techniques were present. The term FFF was initially used as an unconstrained alternative given the fact that FDM is a trademarked term.
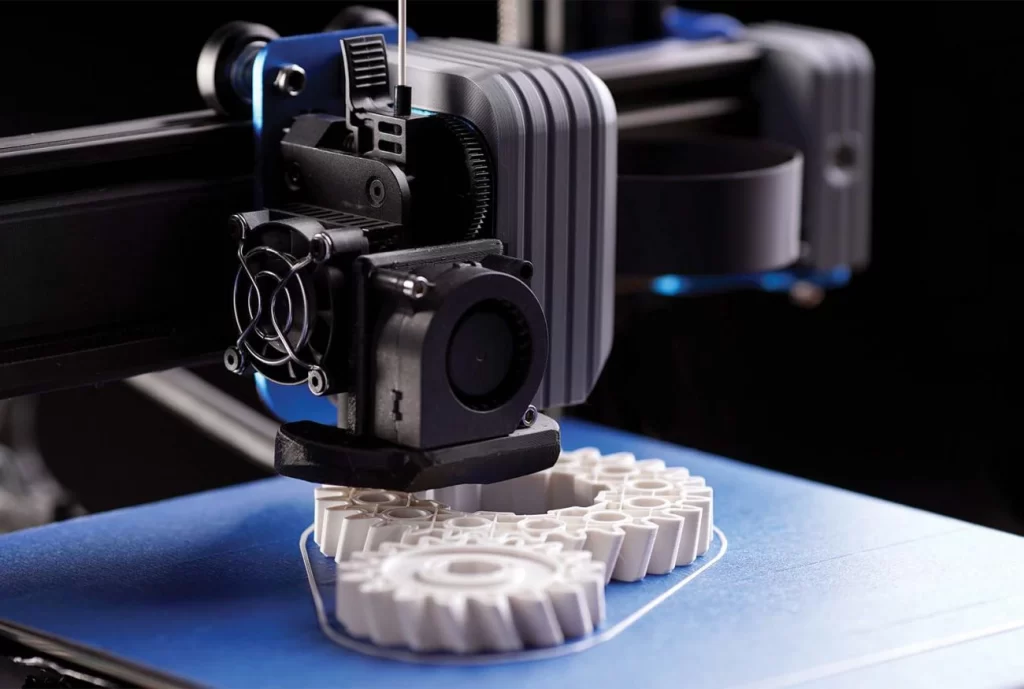
To begin with, an extrusion heated nozzle moves over a built platform, at the same time releases molten plastic, then this begins to deposit the thermoplastic material in thin layers, one on top of another onto a print bed, which is where eventually the 3D printed object is formed. The nozzle and the printed bed move while at the same time the plastic is being extruded. In this process, the slicing software is crucial due to this being the one that separates the design into different layers for 3D printing optimization.
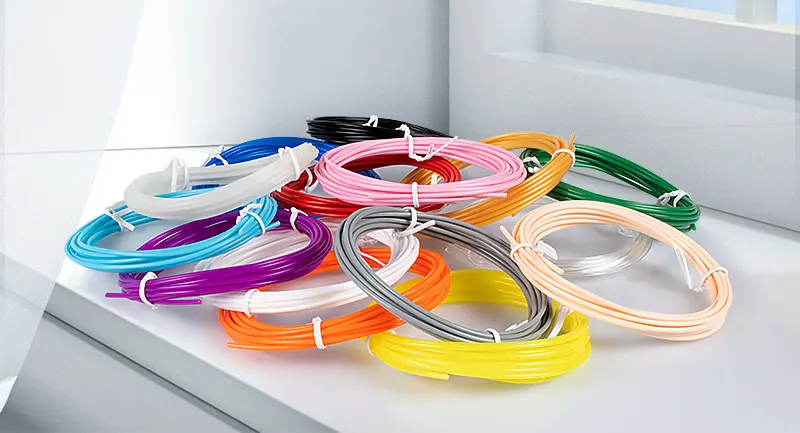
3D printing uses a wide range of different variations of materials such as pastes, raw materials, and thermoplastics or filaments, being these the most used and come in different colors, thickness, and sizes to fit the purpose of the 3D printing model. Filament materials used for extrusion include thermoplastics, ABS, PLA, HIPS, TPU, ASA, PETG, PLA, etc.