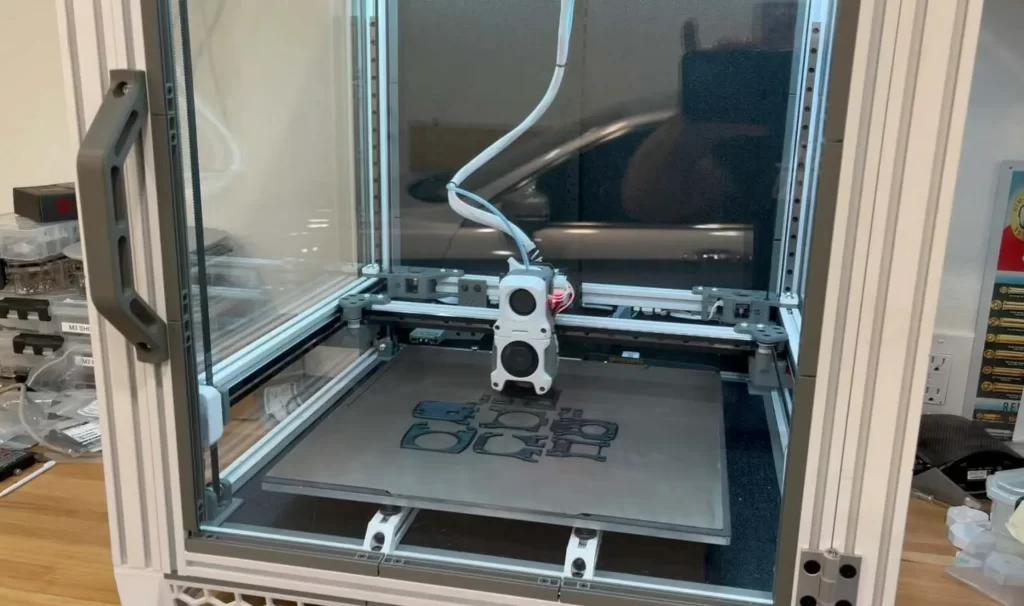
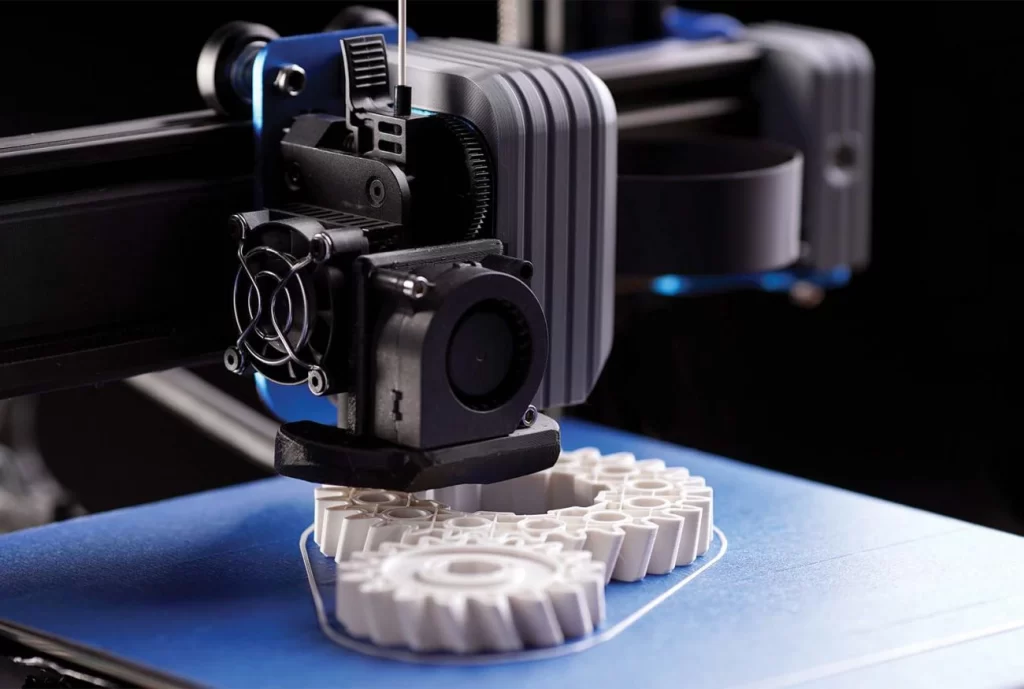
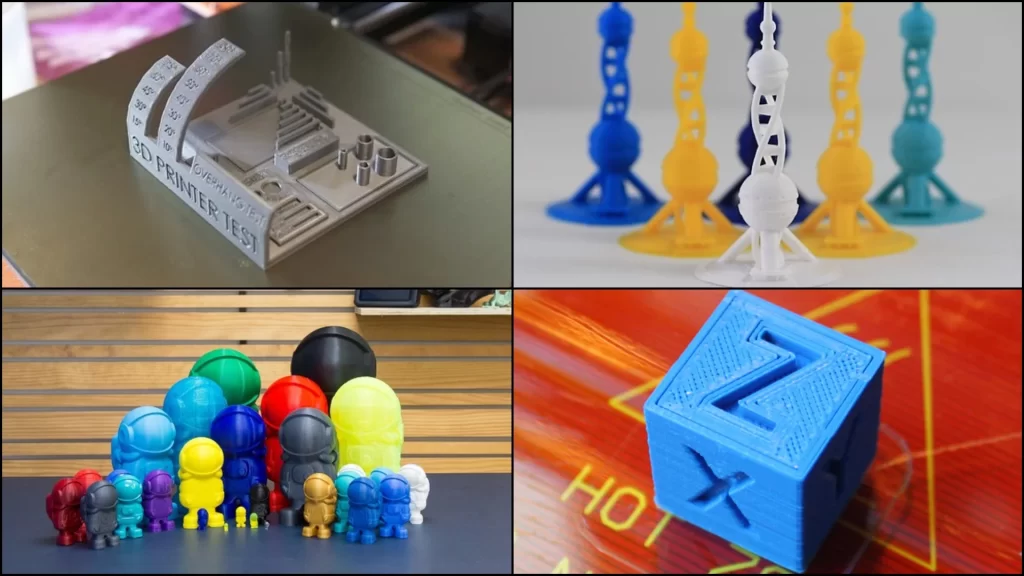
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that uses thin layers of filament (in most cases, plastic) to create a physical object from a three-dimensional model. A digital file creates the model which eventually transfers to the printer. The 3D printer creates thin layers, one on top of another, until a 3D printed object is formed. 3D printing also allows the production of models of more complex shapes with less material than traditional manufacturing techniques.
Research shows that 3D printing history starts in the ’70s. It was not until 1980 that early additive manufacturing equipment and materials were developed. Hideo Kodama initiated a patent for this technology but, unfortunately, never commercialized it. In the ’90s 3D printing began to attract attention from technologies around the world. These years also saw the invention of fully functional human organs for transplants in young patients using 3D printed methods covered with particles and cells from their very own body. It was a major success for the medical industry.
Despite these advancements, 3D printing had limited functional productions until the 2000s, when additive manufacturing gained popularity. Additive Manufacturing is the process of adding materials together to produce an item. The procedure of additive manufacturing is in stark contrast to the concept of subtractive manufacturing. Subtractive manufacturing is the process of removing material by carving out a surface to create an object. This process also produces a great deal of material waste. In this regard, the term 3D printing still refers more to technologies that use polymer materials and, additive manufacturing refers more to metalworking. But by the early 2010s, the terms of these two processes were used in popular language across the market, media, companies, and manufacturers.
Around 2008 the first self-replicating 3d printer model was created. That means a 3D printer was able to recreate itself by printing its parts and components. This enabled users to produce more printers for others. Studies show that later the same year, a person successfully walked with a 3D printed prosthetic leg fully printed in one piece. Then in the 2010’s the additive processes matured, and 3D printing work began to create objects layer by layer. In 2012, with the addition of plastic and other various materials for 3D printing, several authors began to think that 3D printing could be important for a developing world.
During the following years, more applications for 3D printing have emerged, including the world’s first aircraft. Makers using 3D printers agree that this method is faster and cheaper compared to traditional methods and are ideal for those who need rapid prototyping (RP). Terms such as desktop manufacturing, rapid manufacturing, and rapid prototyping have since become synonymous with 3D printing.
The market offers a wide variety of 3D printers. Sophisticated machines are expensive, but there are also more affordable models available with high-quality printing and features. 3D printing also offers easy-to-use desktop printers, which are increasingly popular among schools and engineers.